APrf John Semmler
Associate Professor
School of Pharmacy and Biomedical Sciences
College of Health
Eligible to supervise Masters and PhD - email supervisor to discuss availability.
I lead a research team that is internationally recognised for its excellence in pursuing novel research questions using cutting-edge brain stimulation techniques to examine the neurophysiology of human movement throughout the lifespan. My research attracts Category 1 funding, is regularly published in the top journals in the field, and is highly cited internationally. I have a strong record of successful research supervision and training, which includes mentoring externally funded research fellows, graduating numerous PhD students, and regularly supporting honours and undergraduate placements in the laboratory. I am a highly effective teacher with a strong record of education delivery and leadership, where I shape current educational practices in several disciplines, and contribute to high-level program mapping and curriculum design. I also hold numerous senior administration and leadership roles within the University and international research community, including Discipline Lead in Physiology, School Postgraduate coordinator, President of the Australasian Brain Stimulation Society, and hold senior editorial board responsibilities for 3 leading journals in Neuroscience, Physiology and Exercise Science fields.
NEUROPHYSIOLOGY OF HUMAN MOVEMENT GROUP
I am an experienced neurophysiologist and Director of the Neurophysiology of Human Movement group. Research within this group focuses on the neural mechanisms responsible for changes in human movement throughout the life span. We specialise in the use of brain stimulation techniques to painlessly and non-invasively measure and modify the brain’s control of skeletal muscles under diverse conditions, such as ageing, exercise, training, fatigue and mild traumatic brain injury. The overall goal is to understand how the healthy nervous system functions to control movements in different situations, and how it may adapt in conditions involving neurological or neuromuscular injury.

Neurophysiology of Human Movement Group |
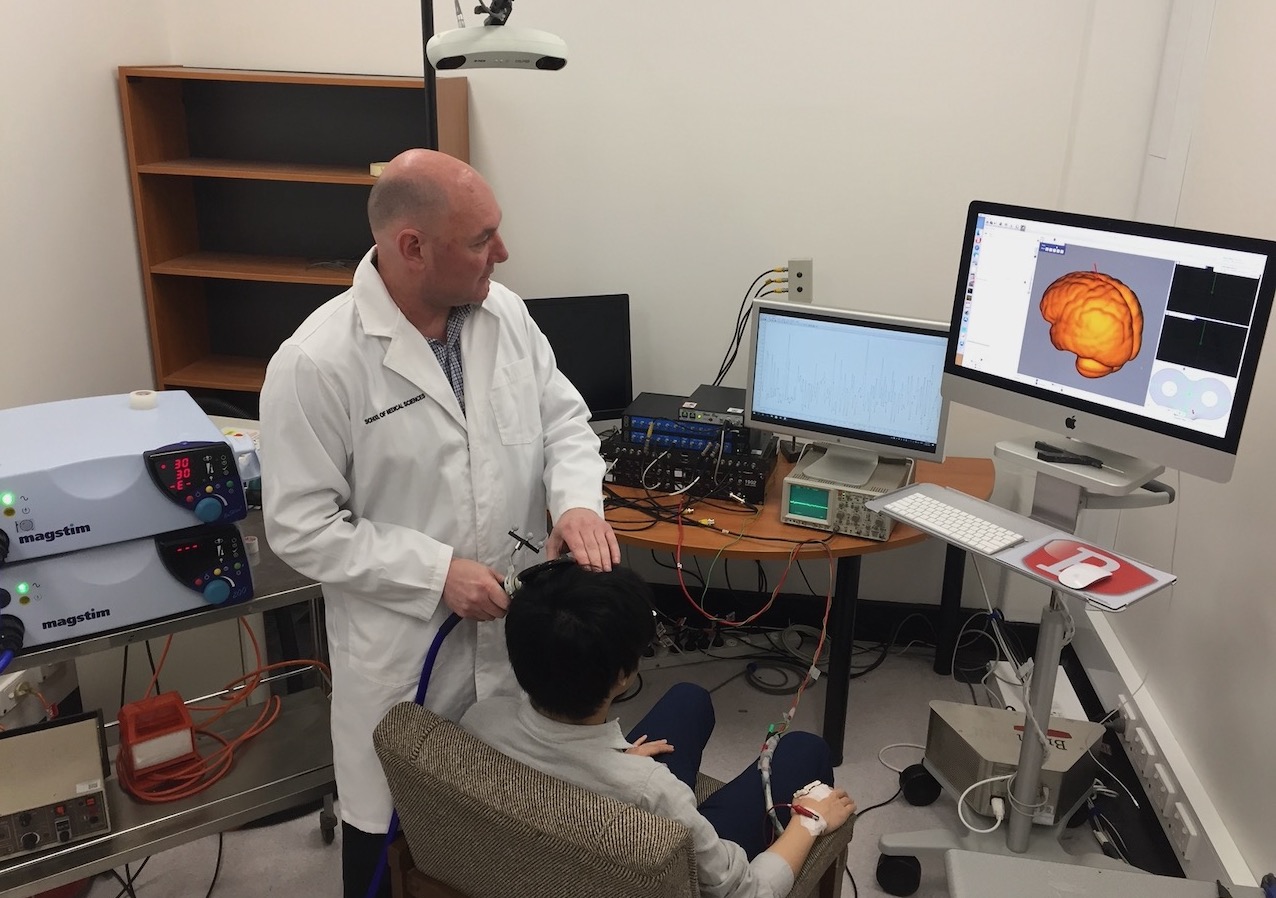
|
AVAILABLE PROJECTS
Project 1
Title: BRAIN OSCILLATIONS AND HUMAN MOVEMENT
Description: Motor areas of the brain oscillate when we move, with different oscillations responsible for different aspects of behaviour. Oscillations in the gamma band (30-90 Hz) play a key role in brain plasticity and motor learning that are thought to be driven by inhibitory circuits. This study will use non-invasive brain stimulation techniques to explore the physiological basis and functional significance of this intriguing brain rhythm, and investigate in new ways how it can be manipulated to improve motor behaviour and learning.
Projects available for: Honours and HDR
Location: Helen Mayo Building (Frome Rd)
Research project start: Semester 1 and 2
Special Requirements: None.
Project 2
Title: BRAIN PLASTICITY AND MOTOR FUNCTION IN OLDER ADULTS
Description: Recent studies from our group show that specific brain circuits important for motor system plasticity are altered in older adults. Do changes in these circuits contribute to impaired motor performance and learning in older adults? Can we modify plasticity and learning by strengthening these circuits in older adults? Several studies using brain stimulation and electroencephalography (EEG) in human participants are planned to address these research questions.
Projects available for: Honours and HDR
Location: Helen Mayo Building (Frome Rd)
Research project start: Semester 1 and 2
Special Requirements: None.
Project 3
Title: NEUROPHYSIOLOGY OF EXERCISE
Description: It is now well accepted that physical activity and exercise is capable of providing benefits to the central nervous system (CNS) that can maintain or enhance brain and motor function. However, it is not known whether different features of the exercise (intensity, duration, type) influence brain function (excitability, connectivity, plasticity), or whether this can be harnessed to improve motor function. Several studies using brain stimulation, electroencephalography (EEG) and motor skill learning will be performed to examine the neural mechanisms that influence brain and motor function with different types of exercise in humans.
Projects available for: Honours and HDR
Location: Helen Mayo Building (Frome Rd)
Research project start: Semester 1 and 2
Special Requirements: None.
Project 4
Title: IMPROVING MOTOR SKILL LEARNING IN HUMANS
Description: The ability to learn new motor skills is a fundamental requirement for participation in modern society, but this ability often deteriorates with neurological injury. Many factors are known to influence motor skill learning even in healthy individuals, such as practice structure, fatigue, handedness, exercise, gender and advancing age. The aim of this project is to explore one or more of these factors in an effort to understand the parameters that produce the optimum conditions for improved motor skill learning in humans.
Projects available for: Undergraduate
Location: Helen Mayo Building (Frome Rd)
Research project start: Semester 1 or 2
Special Requirements: None.
| Date | Position | Institution name |
|---|---|---|
| 2023 - ongoing | Discipline Lead in Physiology | The Univeristy of Adelaide |
| 2022 - ongoing | University Research Integrity Assessment Officer | University of Adelaide |
| 2022 - ongoing | Postgraduate Coordinator | University of Adelaide |
| 2021 - ongoing | Royal Australasian College of Dental Surgeons Primary Examiner | Royal Australasian College of Dental Surgeons (RACDS) |
| 2015 - ongoing | Associate Professor | University of Adelaide |
| 2008 - 2014 | Senior Lecturer | The University of Adelaide |
| 2005 - 2007 | Lecturer | The University of Adelaide |
| 2003 - 2005 | Senior Lecturer | Deakin University |
| 1997 - 2002 | Postdoctoral Fellow | University of Colorado Boulder |
| 1996 - 1997 | Research Associate | The University of Adelaide |
| Date | Institution name | Country | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1993 - 1997 | The University of Adelaide | Australia | PhD |
| 1992 - 1992 | The University of Adelaide | Australia | B.Sc. (Hons) |
| 1989 - 1991 | University of South Australia | Australia | B. Appl. Sc (Exercise Science) |
| Year | Citation |
|---|---|
| 2019 | Otieno, L. A., Semmler, J., & Sidhu, S. (2019). Age-related changed in GABA-mediated inhibition with fatiguing single joint exercise.. In Proceedings of the ANS Sensorimotor Control Satellite Meeting. Adelaide. |
| 2011 | Trinder, J., Nicholas, C., Heckel, L., Jordan, A., Woods, M., Waloszek, J., . . . Semmler, J. (2011). Common pre-motor drive to genioglossus and tensor palatini motor neurons. In JOURNAL OF SLEEP RESEARCH Vol. 20 (pp. 19-20). Sydney, AUSTRALIA: WILEY-BLACKWELL. |
| Year | Citation |
|---|---|
| - | Liao, W. -Y., Opie, G., Semmler, J., & Ziemann, U. (n.d.). Data_deidentified.xlsx. DOI |
| Year | Citation |
|---|---|
| 2025 | Gamage, N., Altheyab, A., Guo, Y., Phillips, B., Opie, G., Semmler, J., . . . Piasecki, M. (2025). Bilateral neuromuscular adaptation to acute unilateral resistance exercise in healthy older adults. DOI |
| 2024 | Gamage, N., Liao, W. -Y., Hand, B., Atherton, P., Piasecki, M., Opie, G., & Semmler, J. (2024). Theta-gamma transcranial alternating current stimulation enhances motor skill acquisition in healthy young and older adults. DOI |
| 2024 | Liao, W. -Y., Opie, G., Ziemann, U., & Semmler, J. (2024). Modulation of dorsal premotor cortex disrupts neuroplasticity of primary motor cortex in young and older adults. DOI |
| 2023 | Biabani, M., Fornito, A., Goldsworthy, M., Thompson, S., Graetz, L., Semmler, J., . . . Rogasch, N. (2023). Characterising the contribution of auditory and somatosensory inputs to TMS-evoked potentials following stimulation of prefrontal, premotor and parietal cortex. DOI Europe PMC1 |
| 2023 | Sghirripa, S., Graetz, L., Semmler, J., Sutton, R., Williams, E. E. R., & Goldsworthy, M. (2023). Age-Related Differences in Alpha Power for Distractor Inhibition During Visual Working Memory. DOI |
| 2022 | Sghirripa, S., Semmler, J., & Goldsworthy, M. (2022). Age-Related Changes in Visual Working Memory Consolidation. DOI |
I have received regular support from major funding bodies (ARC, NHMRC, NIH) and have attracted ~$4 million in research funding.
Recent grants include:
2025-2028: ARC Discovery Project (DP250101672). CIA. (JG Semmler, G Opie, U Ziemann) $574,888
Title: Synchronised brain oscillations and motor function in older adults.
2024: Neurosurgical Research Foundation. CIB. (G Opie, JG Semmler) $47,112
Title: Modulating the shape of brain oscillations to drive clinical benefits in Parkinson's disease.
2020-2025: ARC Discovery Project (DP200101009). CIA. (JG Semmler, U Ziemann, G Opie) $297,621
Title: Reconnecting the ageing brain to enhance plasticity and motor learning.
2023: Faculty of Health and Medical Science Research Infrastructure Award. CIB. $74,657
2023: Faculty of Health and Medical Science Research Infrastructure Award. One of 9 CIs. $86,874
2022: University DVCR Small Equipment Support. Sole-CI $10,164
2022: Australian Brain Foundation. CIB. (GM Opie, JG Semmler & N Foo) $40,000
Title: How do changes in brain rhythms contribute to the effects of brain injury?
2022: Faculty of Health and Medical Science Research Infrastructure Award. CIB. $87,303
2021: Faculty of Health and Medical Science Research Infrastructure Award. CIB. $46,000
2021: Faculty of Health and Medical Science Research Infrastructure Award. One of 13 CIs $104,000
2021: AMS/Biomedicine Small Equipment Grant Award. CIA. $4,650
2019: Faculty of Health and Medical Science Research Infrastructure Award. CIB. $47,652
2015-2019: ARC Discovery Project (DP150100930). CIA. (JG Semmler, MC Ridding, U Ziemann) $266,300
Title: Boosting brain plasticity and motor function in older adults
I have developed and transformed a wide variety of courses in Health Sciences (BHMS), Medicine (MBBS/BMD) and Dentistry (BDS). Recent teaching includes significant contributions to Physiology 2A (200-330 BHMS students, 2014-current), Neuromotor Control (65-130 BHMS students, 2014-current), Dental Science and Practice I and II (~80 BDS students, 2008-current), Foundations of Medicine (~170 MBBS/BMD students), and Medical Studies 2A (~165 MBBS/BMD students). My physiology teaching is internationally recognised in Dentistry by an appointment as a Physiology Examiner for the Royal Australasian College of Dental Surgeons (RACDS). I also make contributions at a Program level through my role as an Academic Transition Panel member/Program Champion for Health (Human Performance) and Course Designer in the Health Tranche for the new Adelaide University.
| Date | Role | Research Topic | Program | Degree Type | Student Load | Student Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2025 | Principal Supervisor | Synchronised brain oscillations and motor function | Doctor of Philosophy | Doctorate | Full Time | Mr Noah Jared Tilley |
| 2025 | Co-Supervisor | Characterising the neural processes mediating response inhibition. | Doctor of Philosophy | Doctorate | Full Time | Mr Giuseppe Rinaldi |
| 2025 | Principal Supervisor | Synchronised brain oscillations and motor function | Doctor of Philosophy | Doctorate | Full Time | Mr Noah Jared Tilley |
| 2025 | Co-Supervisor | Characterising the neural processes mediating response inhibition. | Doctor of Philosophy | Doctorate | Full Time | Mr Giuseppe Rinaldi |
| 2024 | Principal Supervisor | Targeting brain oscillations for human movement | Doctor of Philosophy | Doctorate | Full Time | Amy Charlotte Meadows |
| 2024 | Principal Supervisor | Targeting brain oscillations for human movement | Doctor of Philosophy | Doctorate | Full Time | Amy Charlotte Meadows |
| 2023 | Co-Supervisor | Investigating neuronal oscillations and motor function in older adults | Doctor of Philosophy | Doctorate | Full Time | Ms Ekaterina Voevodina |
| 2023 | Co-Supervisor | Investigating neuronal oscillations and motor function in older adults | Doctor of Philosophy | Doctorate | Full Time | Ms Ekaterina Voevodina |
| 2022 | Co-Supervisor | Investigating the role of neuronal oscillatory interactions within the physiological and functional effects of mTBI | Doctor of Philosophy | Doctorate | Part Time | Miss Emily Moore |
| 2022 | Co-Supervisor | Investigating the role of neuronal oscillatory interactions within the physiological and functional effects of mTBI | Doctor of Philosophy | Doctorate | Part Time | Miss Emily Moore |
| 2021 | Principal Supervisor | Interventions to manipulate neuroplasticity in ageing | Doctor of Philosophy under a Jointly-awarded Degree Agreement with | Doctorate | Full Time | Mrs Nishadi Nivanthika Hirimbura Gamage |
| 2021 | Principal Supervisor | Interventions to manipulate neuroplasticity in ageing | Doctor of Philosophy | Doctorate | Full Time | Mrs Nishadi Nivanthika Hirimbura Gamage |
| Date | Role | Research Topic | Program | Degree Type | Student Load | Student Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 - 2024 | Principal Supervisor | MODULATING CORTICAL PLASTICITY AND CONNECTIVITY TO IMPROVE MOTOR LEARNING IN OLDER ADULTS | Doctor of Philosophy | Doctorate | Full Time | Mr Wei-Yeh Merrick Liao |
| 2019 - 2022 | Principal Supervisor | Brain Rhythms and Working Memory in Healthy Ageing | Doctor of Philosophy | Doctorate | Full Time | Miss Sabrina Sghirripa |
| 2018 - 2022 | Principal Supervisor | Impact of Fatiguing Exercise on Corticospinal Excitability and Motor Performance in Young and Older Adults | Doctor of Philosophy | Doctorate | Full Time | Miss Lavender Achieng Otieno |
| 2018 - 2022 | Principal Supervisor | Motor Cortex Plasticity and Skill Acquisition in Endurance-Trained Athletes | Doctor of Philosophy | Doctorate | Full Time | Mr Brodie Hand |
| 2012 - 2015 | Principal Supervisor | Investigating Intracortical Inhibitory Mechanisms Contributing to Age-related Deficits in Motor Function | Doctor of Philosophy | Doctorate | Full Time | Dr George McKenzie Opie |
| 2010 - 2012 | Principal Supervisor | Human Motor Cortex Plasticity Induction is Influenced by Multiple Factors | Doctor of Philosophy | Doctorate | Full Time | Mr John Cirillo |
| 2006 - 2008 | Co-Supervisor | High Protein Dietary Patterns and Type 2 Diabetes | Doctor of Philosophy | Doctorate | Full Time | Mrs Karma Louise Pearce |
| 2006 - 2010 | Principal Supervisor | Motor Unit Activity and Neuromuscular Function after Exercise-Induced Damage to Elbow Flexor Muscles | Doctor of Philosophy | Doctorate | Full Time | Ms Tamara Dartnall |
| Date | Role | Research Topic | Location | Program | Supervision Type | Student Load | Student Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2024 - 2024 | Principal Supervisor | Theta-gamma tACS and visuomotor skill learning | The University of Adelaide | BHMS(Hons) | Honours | Full Time | Noah Tilley |
| 2023 - 2023 | Co-Supervisor | Brain Function after mild traumatic brain injury | The University of Adelaide | BHMS(Hons) | Honours | Full Time | Emily Webb |
| 2023 - 2023 | Principal Supervisor | Gamma tACS and motor skill learning | The university of Adelaide | BHMS(Hons) | Honours | Full Time | Monty Clark |
| 2023 - 2023 | Principal Supervisor | Gamma tACS, intracortical inhibition and motor cortical plasticity | The University of Adelaide | BHMS(Hons) | Honours | Full Time | Nicholas Nyskohus |
| 2021 - 2022 | Co-Supervisor | Brain Function and Concussion | The University of Adelaide | BHMS(Hons) | Honours | Full Time | Emily Moore |
| 2021 - 2021 | Co-Supervisor | Ageing, Brain Plasticity and Different Cortical Circuits | The University of Adelaide | BHMS(Hons) | Honours | Full Time | Giuseppe Rinaldi |
| 2020 - 2020 | Co-Supervisor | Cerebellar and Motor cortex connectivity | The University of Adelaide | BHMS(Hons) | Honours | Full Time | Wei-Yeh Liao |
| 2017 - 2017 | Co-Supervisor | Fatigue and Intracortical Inhibition | The university of Adelaide | BHMS(Hons) | Honours | Full Time | Lavender Otieno |
| 2017 - 2017 | Principal Supervisor | Priming brain stimulation and motor cortex plasticity in older adults | The University of Adelaide | BHMS(Hons) | Honours | Full Time | Brodie Hand |
| 2016 - 2016 | Co-Supervisor | tDCS and intracortical inhibition during cycling | The University of Adelaide | BHMS(Hons) | Honours | Full Time | Thomas Quaglia |
| 2015 - 2015 | Principal Supervisor | Priming brain stimulation and motor cortical plasticity | The University of Adelaide | BHMS(Hons)) | Honours | Full Time | Eleni Vosnakis |
| 2014 - 2014 | Principal Supervisor | Exercise intensity and brain plasticity | The University of Adelaide | BHMS(Hons) | Honours | Full Time | Alexander O'Dea |
| 2014 - 2014 | Co-Supervisor | TMS and neuroplasticity | The University of Adelaide | BHMS(Hons) | Honours | Full Time | Harleen Kaur |
| 2013 - 2013 | Principal Supervisor | Immobilisation, plasticity and motor performance | The University of Adelaide | BHMS(Hons) | Honours | Full Time | Alexandra Evans |
| 2012 - 2012 | Co-Supervisor | Brain stimulation and motor cortical excitability | The University of Adelaide | BHMS(Hons) | Honours | Full Time | Kathryn Dansie |
| 2011 - 2011 | Principal Supervisor | Motor cortex plasticity and sleep apneoa | The University of Adelaide | BHMS(Hons) | Honours | Full Time | George Opie |
| 2010 - 2010 | Principal Supervisor | Motor cortical plasticity and ageing | The University of Adelaide | BHMS(Hons) | Honours | Full Time | Lisa Kurylowicz |
| 2010 - 2010 | Principal Supervisor | Eccentric exercise and intracortical inhibition | The University of Adelaide | BHMS(Hons) | Honours | Full Time | Bradley Pitmann |
| 2008 - 2008 | Principal Supervisor | Eccentric muscle damage and muscle activation strategies | The University of Adelaide | BHMS(Hons) | Honours | Full Time | Sonja Ebert |
| 2007 - 2007 | Principal Supervisor | Low frequency fatigue and neuromuscular performance | The Univeristy of Adelaide | BHMS(Hons) | Honours | Full Time | James Dundon |
| 2006 - 2006 | Principal Supervisor | Eccentric muscle damage and anisometric contractions | The University of Adelaide | BHMS(Hons) | Honours | Full Time | Tanya Turner |
| Date | Role | Committee | Institution | Country |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 - ongoing | Member | School of Biomedicine Executive Committee | The Univeristy of Adelaide | Australia |
| 2020 - ongoing | Member | Adelaide Medical School Research Committee | The University of Adelaide | Australia |
| 2013 - 2014 | Chair | Human Research Ethics Committee | University of Adelaide | Australia |
| 2006 - 2014 | Member | Human Research Ethics Committee | University of Adelaide | - |
| Date | Role | Membership | Country |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 - ongoing | Member | Australasian Cognitive Neurosicence Society | Australia |
| 2018 - ongoing | Member | Australasian Brain Stimulation Society | Australia |
| 2004 - 2015 | Member | American Physiological Society | United States |
| 2004 - 2004 | Member | Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology | United States |
| 1999 - 2011 | Member | American College of Sports Medicine | United States |
| 1998 - 2019 | Member | Society for Neuroscience | United States |
| 1992 - 1997 | Member | Australian Physiological and Pharmacological Society | Australia |
| 1992 - ongoing | Member | Australasian Neuroscience Society | Australia |
| Date | Role | Editorial Board Name | Institution | Country |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2024 - ongoing | Associate Editor | Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience | N/A | Switzerland |
| 2020 - ongoing | Board Member | Experimental Brain Research | - | Germany |
| 2006 - ongoing | Board Member | Journal of Applied Physiology | - | United States |
| Date | Office Name | Institution | Country |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2025 - 2027 | President of the Australasian Brain Stimulation Society | None | Australia |




